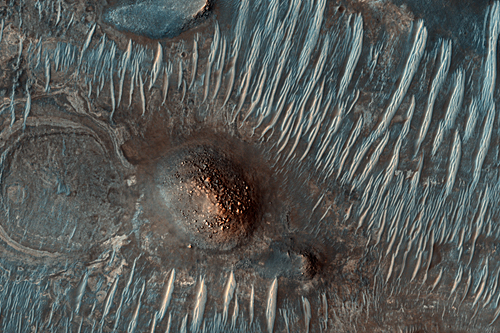
Mars has some fascinating a beautiful craters, but are all craters the same, or are there aspects that make each one unique? NASA's MRO has a closer look wit. The High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter captured these sand ripples and the large dune (at center) on Feb. Color has been a. HiRISE - High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment.The High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment Camera is a camera o.
Made with HiRISE MarsPoetica Social Media Map The BeautifulMars eBook Series The BeautifulMars Podcast Our Volunteers: Camera Specs CTX Directory PDS Directory Science Themes Software Lunar & Planetary Laboratory PIRL College of Science University of Arizona MRO NASA/JPL Planet Four High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment HiRISE Operations. HiRISE is the most powerful camera ever sent to another planet. From on-board NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, HiRISE (High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment) observes the Martian surface at resolutions down to 25 cm/pixel, in three wavelengths and in stereo.
Hirise Mars
March 04, 2021
The High-Resolution Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera aboard NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) took this image of the Perseverance rover on Feb. 24, 2021. The false-color image shows a ring of blast marks where thrusters from the rover’s descent stage blew away dust during landing on Feb. 18, 2021.

By rolling MRO to the side (18 degrees for this image) as it passes over Perseverance every few days, the mission team enables HiRISE to see the rover. Perseverance is about 10 feet by 9 feet (3 by 2.7 meters) in size and is about 180 miles (290 kilometers) away from HiRISE in this image.

MRO’s mission is managed by NASA‘s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. Lockheed Martin Space in Denver built the spacecraft. The University of Arizona in Tucson provided and operates HiRISE.

Embed this resource by pasting the following code into your website:
February 19, 2021
The descent stage holding NASA’s Perseverance rover can be seen falling through the Martian atmosphere, its parachute trailing behind, in this image taken on Feb. 18, 2021, by the High Resolution Imaging Experiment (HiRISE) camera aboard the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The ancient river delta, which is the target of the Perseverance mission, can be seen entering Jezero Crater from the left.
HiRISE was approximately 435 miles (700 kilometers) from Perseverance and traveling at about 6750 mile per hour (3 kilometers per second) at the time the image was taken. The extreme distance and high speeds of the two spacecraft were challenging conditions that required precise timing and for Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter to both pitch upward and roll hard to the left so that Perseverance was viewable by HiRISE at just the right moment.
Hirise Mars Photos
The orbiter’s mission is led by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. JPL, a division of Caltech, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. Lockheed Martin Space in Denver, built the spacecraft. The University of Arizona provided and operates HiRISE.

Hirise Mars Resolution
Embed this resource by pasting the following code into your website:
